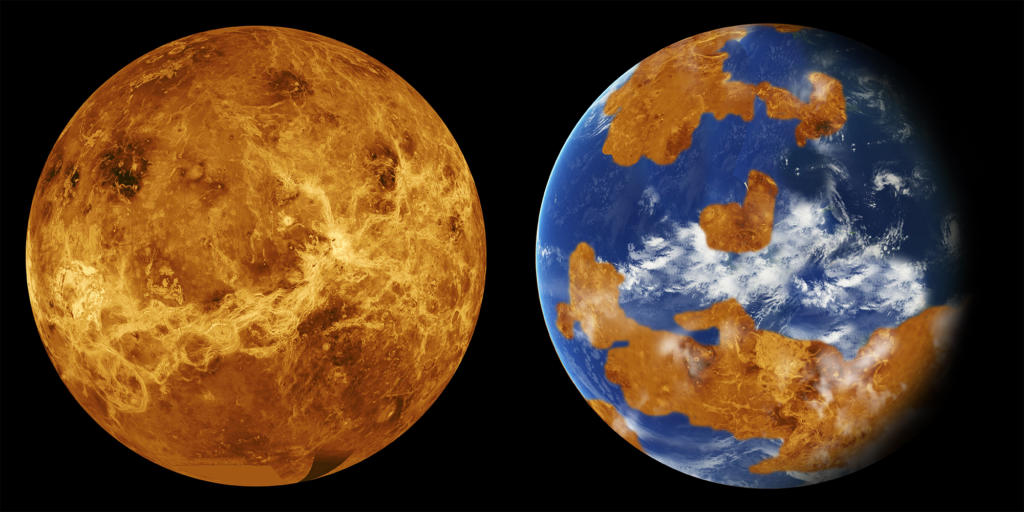
We may be taught a lot about native climate change from Venus, our sister planet. Venus for the time being has a flooring temperature of 450℃ (the temperature of an oven’s self-cleaning cycle) and an surroundings dominated by carbon dioxide (96 per cent) with a density 90 situations that of Earth’s.
Venus is a extremely uncommon place, utterly uninhabitable, moreover possibly inside the clouds some 60 kilometres up the place the present discovery of phosphine may counsel floating microbial life. Nevertheless the ground is totally inhospitable.
However, Venus as quickly as in all probability had an Earth-like native climate. In step with present native climate modelling, for lots of its historic previous Venus had flooring temperatures very similar to present day Earth. It in all probability moreover had oceans, rain, possibly snow, maybe continents and plate tectonics, and far more speculatively, possibly even flooring life.
Decrease than one billion years up to now, the native climate dramatically modified because of a runaway greenhouse impression. It could be speculated that an intensive interval of volcanism pumped enough carbon dioxide into the surroundings to set off this good native climate change event that evaporated the oceans and prompted the highest of the water cycle.
Proof of change
This hypothesis from the native climate modellers impressed Sara Khawja, a grasp’s pupil in my group (co-supervised with geoscientist Claire Samson), to seek for proof in Venusian rocks for this proposed climatic change event.
Given that early Nineteen Nineties, my Carleton Faculty evaluation crew — and further these days my Siberian crew at Tomsk State Faculty — have been mapping and decoding the geological and tectonic historic previous of Earth’s excellent sister planet.
Soviet Venera and Vega missions of the Nineteen Seventies and Eighties did land on Venus and take photographs and evaluated the composition of the rocks, sooner than the landers failed because of extreme temperature and pressure. However, our most full view of the flooring of Venus has been provided by NASA’s Magellan spacecraft inside the early Nineteen Nineties, which used radar to see by means of the dense cloud layer and produce detailed images of larger than 98 per cent of Venus’s flooring.
Historic rocks
Our look for geological proof of the nice native climate change event led us to take care of the oldest form of rocks on Venus, referred to as tesserae, which have a elaborate look suggestive of an prolonged, troublesome geological historic previous. We thought that these oldest rocks had the easiest likelihood of preserving proof of water erosion, which is such an important course of on Earth and will have occurred on Venus earlier to the nice native climate change event.
Given poor resolution altitude data, we used an indirect technique to aim to acknowledge historic river valleys. We demonstrated that youthful lava flows from the encircling volcanic plains had stuffed valleys inside the margins of tesserae.
To our astonishment these tesserae valley patterns had been much like river transfer patterns on Earth, leading to our suggestion that these tesserae valleys had been formed by river erosion all through a time with Earth-like climate circumstances. My Venus evaluation groups at Carleton and Tomsk State universities are studying the post-tesserae lava flows for any geological proof of the transition to terribly scorching conditions.
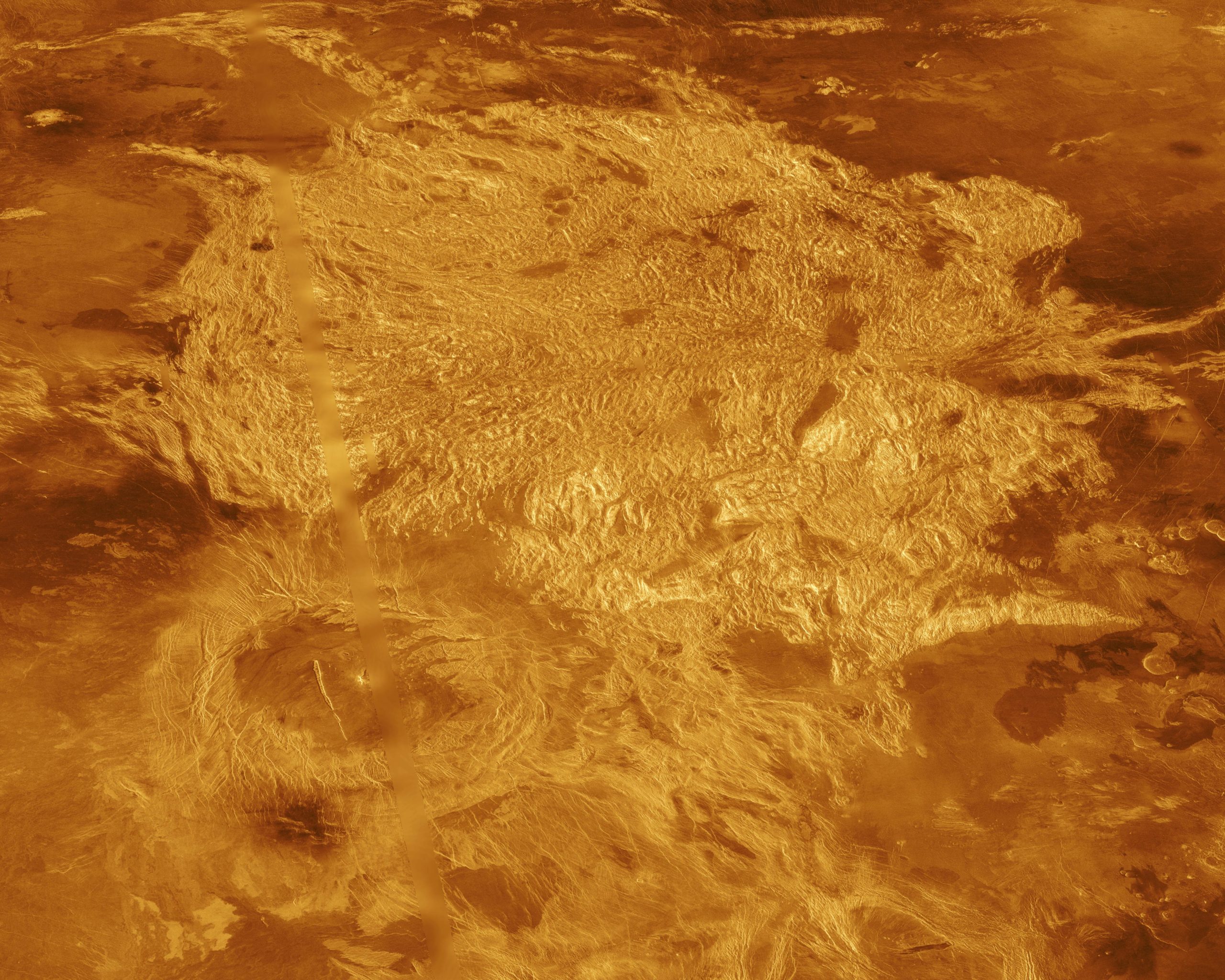
Credit score rating: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Earth analogies
As a technique to understand how volcanism on Venus would possibly produce such a change in native climate, we’re in a position to look to Earth historic previous for analogues. We’re in a position to uncover analogies in super-eruptions like the ultimate eruption at Yellowstone that occurred 630,000 years.
Nevertheless such volcanism is small compared with huge igneous provinces (LIPs) that occur roughly every 20-30 million years. These eruption events can launch enough carbon dioxide to set off catastrophic native climate change on Earth, along with mass extinctions. To current you a manner of scale, ponder that the smallest LIPs produce enough magma to cowl all of Canada to a depth of about 10 metres. The most important acknowledged LIP produced enough magma which will have coated an area the size of Canada to a depth of virtually eight kilometres.
The LIP analogues on Venus embrace specific individual volcanoes which may be as a lot as 500 kilometres all through, in depth lava channels that attain as a lot as 7,000 kilometres prolonged, and there are moreover associated rift strategies — the place the crust is pulling apart — as a lot as 10,000 kilometres prolonged.
If LIP-style volcanism was the rationale for the nice native climate change event on Venus, then would possibly comparable native climate change happen on Earth? We’re ready to consider a state of affairs many lots of of hundreds of years eventually when a lot of LIPs randomly occurring on the an identical time would possibly set off Earth to have such runaway native climate change leading to conditions like present-day Venus.
This textual content is republished from The Dialog beneath a Inventive Commons license.