Scorpius is a constellation recognized for its distinctive type and for being considered one of many 13 constellations of the zodiac, a belt-shaped area of the night sky that the photo voltaic, moon, and planets appear to maneuver by the use of.
It’s among the many brightest constellations inside the night sky. The title is Latin for scorpion, or really translated as a result of the “creature with the burning sting.”
The place is the Scorpius constellation?
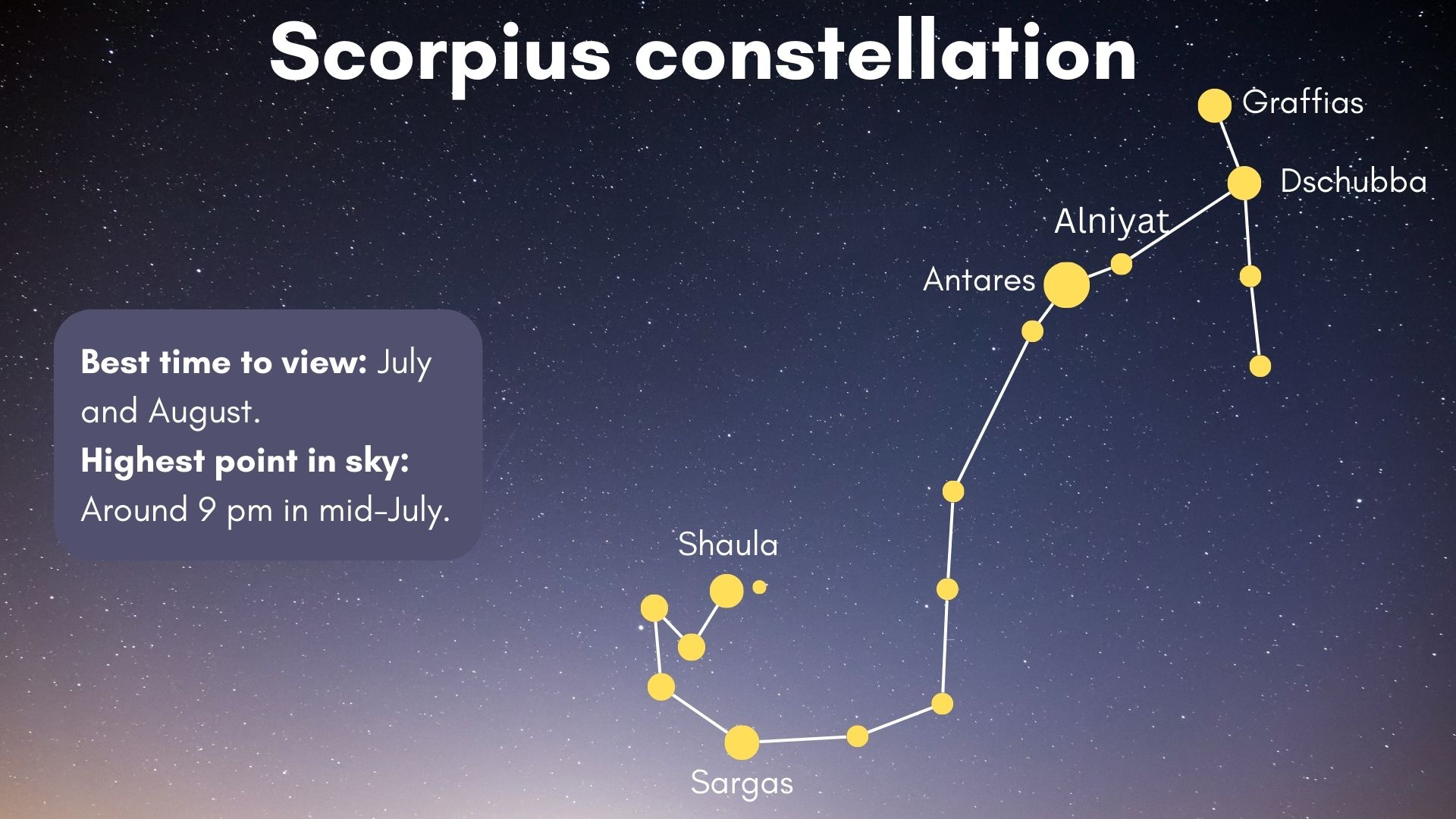
You’ll see all or a couple of of Scorpius from the Southern Hemisphere and much of the mid-Northern Hemisphere between Might and August. Whereas it appears extreme inside the sky inside the center of the Milky Method inside the Southern Hemisphere, it is close to the southern hemisphere in places the place it is seen inside the Northern Hemisphere. Because of its unusual type and relative brightness, Scorpius simply is not robust to establish. In each hemisphere, the best time to view the constellation is July and August, and it is at its highest stage spherical 9 pm in mid-July, in accordance with EarthSky.
What variety of stars does Scorpius have?
Scorpius has 18 named stars, along with Antares, the so-called “rival of Mars,” a pink huge star named for its vivid hue, and Shaula and Lesath, sometimes referred to as the “Cat’s Eyes” because of they’re so shut collectively. It moreover has 14 stars recognized to have planets orbiting them. One in every of these, PSR B1620-26 b, is nicknamed “Methuselah” resulting from its extreme earlier age. It’s estimated to be 12.2 billion years earlier, plus or minus a billion years (for comparability, the universe is estimated to be about 13.8 billion years earlier). The constellation may also be dwelling to doubtlessly habitable planets, along with some orbiting the pink dwarf star Gliese 667C.
Related: Night sky: What you presumably can see tonight [maps]
Scorpius constellation observing targets
Because of its location near the center of the Milky Method, Scorpius has many desirable objects to observe, along with stars, open and globular clusters, and nebulas. Though some are seen with the naked eye, most revenue from some amount of magnification to view clearly, from a superb pair of binoculars to a small or medium-sized telescope. When you occur to need instruments, our biggest binoculars and biggest telescopes guides may help.
Jargon buster
Magnitude: An object’s magnitude is a measure of how vivid an object appears from Earth. Brightness is measured on a numbered scale, with lower numbers being brighter than larger numbers. And it even goes damaging!
Correct ascension (RA): Correct ascension is the sky’s equal to longitude on Earth, and it helps astronomers discover celestial objects. It covers the east-west path and is measured in hours, minutes and seconds.
Declination (Dec): Declination moreover helps astronomers discover celestial objects inside the sky — it is akin to latitude on Earth. It marks how extreme an object will rise inside the sky, masking the north-south path in gadgets of ranges, arcminutes and arcseconds (60 arcseconds in an arcmin, 60 arcmins in a stage).
Bug Nebula
Bug Nebula
Magnitude: 9.1
Approximate distance from Earth: 3,400 light-years
Location: 17h 13m 44.63s (correct ascension), -37° 06′ 11.3″ (declination)
Additionally known as NGC 6302, Caldwell 69, or the Butterfly Nebula, you presumably can view this object’s stunning “wings” with a pair of 80-mm aperture binoculars or a small telescope, in accordance with The Sky Reside.
Named for its bug or butterfly-like type, it is a planetary nebula, original when a dying pink huge star ejects its outer layers, making a shell of glowing gas. The Bug Nebula may also be referred to as a bipolar planetary nebula resulting from its butterfly or hourglass-like type, which happens when supplies is funneled in route of the poles of the dying star, in accordance with NASA.
Butterfly Cluster
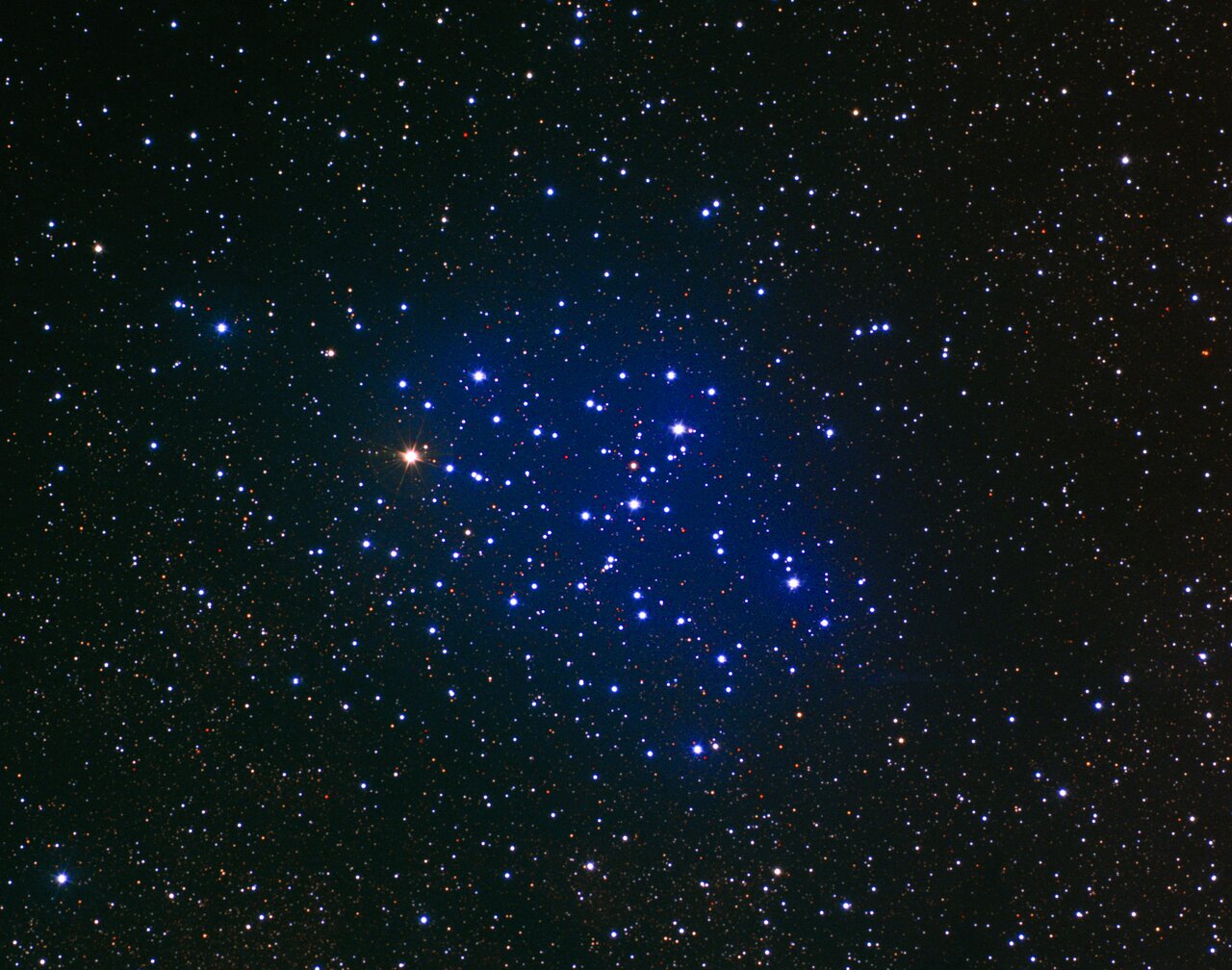

Butterfly Cluster
Magnitude: 4.2
Approximate distance from Earth: 1,590 light-years
Location: 17h 40m 20.7s (correct ascension), -32° 15′ 15″ (declination)
This open cluster of stars, moreover referred to as NGC 6405 or Messier 6, bears a far more imprecise resemblance to the type of a butterfly. This cluster was original from an infinite cloud of gas and dust between 50 and 100 million years prior to now, in accordance with NOIRLab.
Most of its vivid stars are scorching, blue stars with tons between 4 and 5 situations that of our photo voltaic, nonetheless its brightest star is an orange huge, BM Scorpii, in accordance with Messier-Objects.com. In an area with darkish skies, the Butterfly Cluster is just barely seen with the naked eye, nonetheless additional clearly thought-about using a pair of binoculars, in accordance with The Sky Reside.
Ptolemy’s Cluster
Ptolemy’s Cluster
Magnitude: 3.3
Approximate distance from Earth: 980 light-years
Location: 17h 53m 51.2s (correct ascension), -34° 47′ 34″ (declination)
Formally NGC 6475 or Messier 7, this open cluster can merely be seen with the naked eye or with binoculars. Because of its location on the southern tip of Scorpius, it might be onerous to establish inside the Northern Hemisphere, since Scorpius sometimes would not rise all one of the simplest ways above the horizon. In these areas, the best time to view it is within the summertime, when Scorpius reaches its highest prime.
It has been recognized since antiquity and is among the many objects cataloged by the Greek astronomer and mathematician Claudius Ptolemy inside the second century. The cluster has spherical 80 stars, in accordance with Messier-Objects.com.
Messier 4
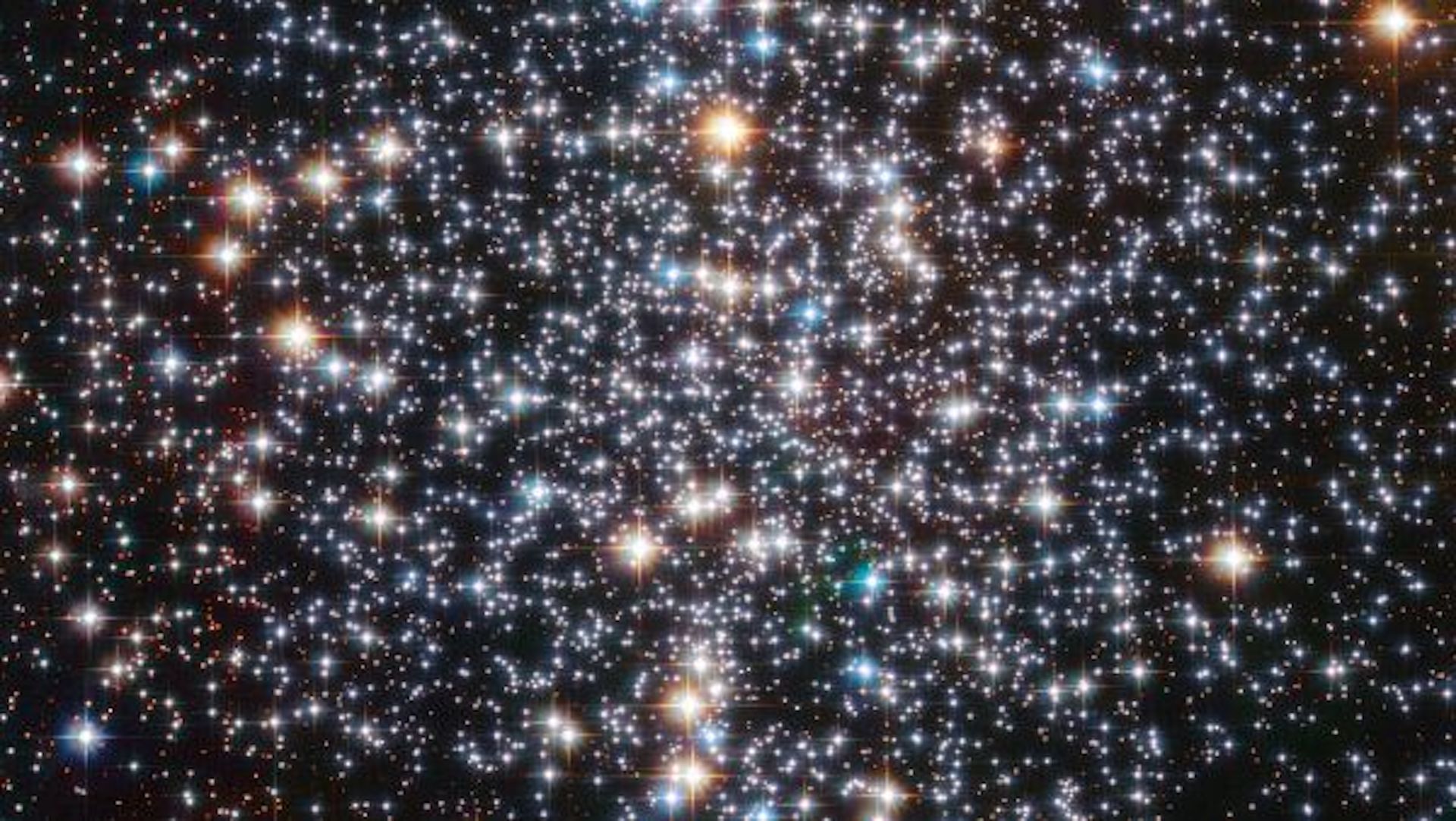

Messier 4
Magnitude: 5.4
Approximate distance from Earth: 6,300 light-years
Location: 16h 23m 35.40s (correct ascension), -26° 31′ 31.9″ (declination)
One in every of numerous objects sometimes referred to as the “Cat’s Eye,” Messier 4, or NGC 6121, is the closest globular cluster to Earth, in accordance with NASA. It might presumably even faintly be seen with the naked eye nonetheless is additional merely seen with binoculars or a small telescope, and is near the pink huge Antares, considered one of many brightest stars inside the sky.
Not like open clusters, globular clusters like this one comprise stars that original at many alternative situations, held together with gravity and with additional stars concentrated at their amenities. Messier 4 incorporates over 100,000 stars, along with 40,000 white dwarfs. These are the standard remnants of stars which have expelled their outer layers. Messier is dwelling to a couple of the oldest astronomical objects recognized, such as a result of the exoplanet “Methuselah,” and will very effectively be as a lot as 13 billion years earlier, in accordance with NASA.
Messier 80
Messier 80
Magnitude: 7.3
Approximate distance from Earth: 28,000 light-years
Location: 16h 17m 02.51s (correct ascension), -22° 58′ 30.4″ (declination)
One among many densest globular clusters inside the Milky Method, this globular cluster incorporates a number of of 1000’s of stars, as per NASA. You need to use a small telescope to establish it, and like quite a lot of Scorpius, it is essentially the most clearly seen in July. In 1860, observers recorded a nova on this cluster, which can happen when a white dwarf collects gas from a close-by star, reigniting the fusion course of that it has prolonged since exhausted. Messer 80 may also be recognized for having an regular amount of stars that are far youthful and additional giant than most of its totally different stars.
Meteor showers and recurring events
Two meteors showers, the Alpha Scorpiids and the Omega Scorpiids, are associated to Scorpius, and are so named because of they appear to radiate from the celebs Alpha Scorpii (Antares) and Omega Scorpii, respectively. The Alpha Scorpiids happen yearly between Might 1 and 31, in accordance with the Custer Observatory. It peaks spherical Might 16. On widespread, 5 meteors are seen per hour all through the bathe’s peak.
The Omega Scorpiids takes place between Might 23 and June 15, in accordance with the Custer Observatory. They’re divided into two showers — the North and South Omega Scorpiids, counting on which hemisphere they’re seen from, and peak spherical June 2. Their peak cost is about 5 meteors per hour.
Scorpius is dwelling to the b star U Scorpii, a recurrent nova and the quickest recognized nova, which experiences eruptions, or flares in brightness, about every ten years. Its most recent eruption was in 2022, in accordance with the American Affiliation of Variable Star Observers.
Scorpius Q&A with an expert

Ashley Pagnotta is an assistant professor on the College of Charleston. Pagnotta’s evaluation pursuits embrace observational astrophysics of novas, supernovas and totally different variable stars.
The place is U Scorpii?
U Scorpii, additionally known as U Sco, is located inside the constellation Scorpius, up near the very best left pincer claw, as you are attempting on the constellation inside the sky.
Two separate — nonetheless very shut — stars make up the system we identify U Sco, and sometimes they are much too faint to see with the unaided eye. Roughly every ten or so years, nonetheless, an eruption referred to as a recurrent nova occurs on the ground of considered one of many stars and the system brightens dramatically. Even at peak brightness, it is not pretty seen to the human eye, nonetheless is effectively contained in the fluctuate of most binoculars (to not level out telescopes), notably from a darkish viewing web site.
What’s a recurrent nova?
A nova is an eruption that occurs on the ground of a white dwarf in a double (or binary) star system. A white dwarf is definitely the ember of a ineffective star — it’s the new, dense, leftover remnant of a low-mass star that has run out of gasoline to keep up nuclear fusion. With no obtainable gasoline left, fusion ceases and the star just isn’t continuously producing vitality.
If the white dwarf is in a binary star system, and if the alternative star inside the binary is shut adequate, the white dwarf can gravitationally pull hydrogen gas from the outer layers of the companion star onto its ground. The gas builds up in a layer on the ground of the white dwarf until it should get scorching and dense adequate on the bottom of that layer for runaway hydrogen fusion to ignite.
The fusion of all of that hydrogen releases an infinite amount of vitality, inflicting the system to quickly get so much brighter, which is what we identify a nova! In most stars, this solely occurs as quickly as every 10,000 or so years, nonetheless in some explicit packages, the nova eruptions happen far more commonly, recurring on a timescale of decrease than about 100 years, subsequently the title recurrent nova.
What causes U Scorpii’s eruptions?
U Sco’s eruptions are attributable to the strategy described above, nonetheless resulting from some express circumstances inside the system, they happen very commonly and pretty repeatedly, about as quickly as every ten years.
The U Sco system consists of a extremely giant white dwarf and a companion star that is starting to switch by the use of the highest ranges of its life. There are two key points going down there.
One, the circumstances on the ground of a high-mass white dwarf like U Sco’s are such that a lot much less hydrogen gas should accumulate sooner than a nova eruption is triggered, and two, as a result of the companion star evolves, it slowly expands, which causes the pace of hydrogen change between the two stars to be larger than regular.
A lot much less mass is required to set off the eruption and that mass is accumulating before common, so there are additional frequent eruptions. On account of the mass of the underlying white dwarf most likely would not change so much all through a single eruption and because the mass change cost may also be comparatively mounted, the time period for the obligatory mass to construct up is pretty fixed, and thus so is the time between eruptions.
How is U Scorpii completely totally different from totally different recurrent novas?
U Sco has the shortest recognized recurrence time of any recurrent nova in our Milky Method Galaxy, and the second-shortest of all recognized recurrent novae. (There is a system inside the shut by Andromeda Galaxy that recurs about yearly!) Because of its transient recurrence time and relatively predictable time between outbursts, now we’ve been able to study it in good component with many alternative telescopes and at many alternative wavelengths, notably all through its 2010 and 2022 outbursts. This has led to a larger understanding of recurrent novae mainly, along with the invention of some sudden, and nonetheless unexplained, outcomes.
Scorpius mythology
Scorpius and Orion are typically intertwined in Greek mythology. Consistent with one fable, Orion boasted that he would kill every animal on the earth. The goddess-hunter Artemis and her mother, Leto, dispatched a scorpion to kill Orion. Zeus put the scorpion inside the heavens after it gained the battle. In a single different fable, the god Apollo, Artemis’s twin brother, grew offended and despatched a scorpion to assault Orion because of he claimed to be a larger hunter than Artemis. Zeus put Orion and Scorpius inside the sky, nonetheless they’re seen at completely totally different situations of the 12 months.
In astrology, which is not a science, the constellation is known as Scorpio. It is the eighth sign inside the Zodiac and represents these born between Oct. 24 and Nov. 22. The traits of those born under the sign are talked about to include dedication and loyalty.
Scorpius simply is not a scorpion to all people. The Javanese people of Indonesia identify this constellation Banyakangrem, meaning “the brooded swan” or Kalapa Doyong, meaning “leaning coconut tree.” In Hawaii, it’s known as the demigod Maui’s Fishhook. In Chinese language language mythology, the constellation was part of the Azure Dragon.
Additional property
Uncover Scorpius in spectacular component on this {{photograph}} printed on NASA. Examine additional regarding the South Omega Scorpiids meteor bathe with these property from UniverseGuide.com. Study additional regarding the Scorpius constellation and the way one can see it within the summertime sky with these property from the Nationwide Science Educating Affiliation.
Bibliography
Messier Objects (2015a). Messier 6: Butterfly Cluster | Messier Objects. [online] www.messier-objects.com. Accessible at: https://www.messier-objects.com/messier-6-butterfly-cluster/[Accessed 26 Jul. 2023].
Messier Objects (2015b). Messier 7: Ptolemy’s Cluster. [online] Messier Objects. Accessible at: https://www.messier-objects.com/messier-7-ptolemys-cluster/
Garner, R. (2023). Messier 80. [online] NASA. Accessible at: https://www.nasa.gov/operate/goddard/2017/messier-80 [Accessed 26 Jul. 2023].
NOIRLab (2020). M6, NGC 6405; Butterfly Cluster. [online] www.noirlab.edu. Accessible at: https://noirlab.edu/public/images/noao-02637/[Accessed 26 Jul. 2023].
McClure, B. (2023). EarthSky | Scorpius? Proper right here’s your constellation. [online] earthsky.org. Accessible at: https://earthsky.org/constellations/scorpius-heres-your-constellation/ [Accessed 26 Jul. 2023].
Popering, D. van (n.d.). Custer Institute. [online] www.custerobservatory.org. Accessible at: https://www.custerobservatory.org/meteors.html [Accessed 26 Jul. 2023].
theskylive.com. (n.d.). Messier 6 (Butterfly Cluster) – Open Cluster in Scorpius | TheSkyLive.com. [online] Accessible at: https://theskylive.com/sky/deepsky/messier-6-butterfly-cluster-object [Accessed 26 Jul. 2023].
theskylive.com. (n.d.). NGC 6302 (Bug Nebula) – Planetary Nebula in Scorpius | TheSkyLive.com. [online] Accessible at: https://theskylive.com/sky/deepsky/ngc6302-bug-nebula-object[Accessed 26 Jul. 2023].
www.aavso.org. (n.d.). U Sco reported in outburst | aavso. [online] Accessible at: https://www.aavso.org/u-sco-june-2022 [Accessed 26 Jul. 2023].