The northern-sky constellation of Gemini is no doubt one of many distinctive constellations listed by Ptolemy throughout the second century, along with one in every of many 12 zodiac constellations.
The phrase “gemini” means twins in Latin; the constellation is said to the Greek mythological twins Castor and Pollux, for whom two of the stars throughout the constellation are named, in accordance with Britannica. (Castor simply is not really a single star, nevertheless a system of six stars that are so shut collectively, they appear as one.)
In numerous historic astrological traditions, the twins are represented by pairs of goats or peacocks, or for various well-known mythological twins like Remus and Romulus.
Gemini will also be recognized for lending its establish to NASA’s Gemini program, so-named for its two-person spacecraft, along with for its Geminga pulsar, distinctive for emitting primarily gamma rays instead of X-rays or seen gentle, in accordance with NASA.
Previous Castor and Pollux, there are eight completely different named stars throughout the Gemini constellation, in accordance with the skywatching website Constellation Data, and fairly a number of deep-sky objects to look at by telescopes. Plus, the radiant degree of the winter Geminid meteor bathe is throughout the constellation.
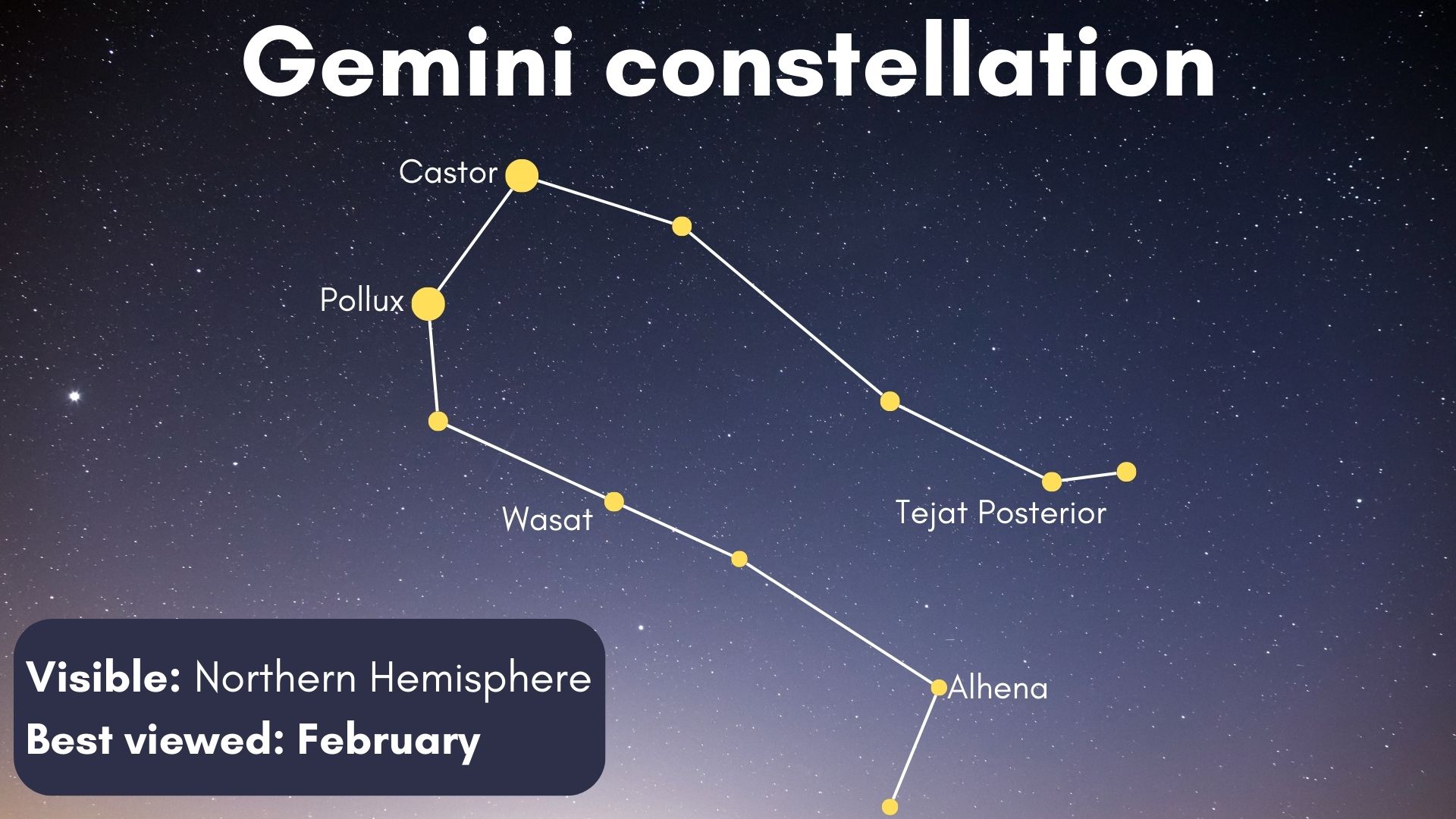
The place is the Gemini constellation?
Gemini takes up 514 sq. ranges of the northern hemisphere’s second quadrant, in accordance with Constellation Data, making it the thirtieth largest constellation. It’s best seen throughout the winter months from the Northern Hemisphere.
You will discover Gemini surrounded by the constellations of Auriga, Orion, Monoceros, Canis Minor, Most cancers, and Lynx. The best approach to identify Gemini is to search out Orion’s Belt, then observe the highway from Rigel (Orion’s correct foot and brightest star), by the belt, and up in course of Betelgeuse (Orion’s left shoulder). Proceed that line, and you could in the end spot Castor and Pollux.
Gemini observing targets
Gemini is full of targets for assertion, every “near” and far. In case you are making an attempt to gear up for a stargazing session, be taught our guides to the best telescopes and best binoculars.
Related: Night time time sky: What you may even see tonight [maps]
Jargon buster
Magnitude: Magnitude is a measure of how shiny an object appears from Earth; the lower an object’s magnitude, the brighter it is. Magnitude might even be measured in antagonistic numbers, which level out elevated ranges of brightness than constructive numbers.
Correct ascension (RA): Correct ascension could also be considered the sky’s mannequin of longitude on Earth. It covers the east-west route and is measured in hours, minutes and seconds. It’s used together with declination to help astronomers discover celestial objects.
Declination (Dec): Declination is much like latitude on Earth. It measures an object’s location throughout the north-south route in ranges, arcminutes and arcseconds (there are 60 arcseconds in an arcmin, 60 arcmins in a degree).
Castor
Castor
Magnitude: 1.58
Approximate distance from Earth: 51 light-years
Location: 7h 34m 25s (correct ascension), +31°53’18″(declination)
Using a telescope, you could zoom in on Castor to distinctly see at least two, usually three, of the six stars that make up the system, in accordance with the Milwaukee Astronomical Society. Impressively, each of these three stars is certainly a double star, though the individual stars are troublesome to discern and never utilizing a really high-powered telescope.
Messier 35 (NGC 2168)
Messier 35 (NGC 2168)
Magnitude: 5.3
Approximate distance from Earth: 2,800 light-years
Location: 6h 8m 54s (correct ascension), +24°20’19” (declination)
Messier 35 is an open cluster of higher than 500 stars that are loosely gravitationally positive. The cluster takes up an area of the sky that’s concerning the similar measurement as a result of the full moon, in accordance with the European Southern Observatory.
Medusa Nebula (Abell 21)
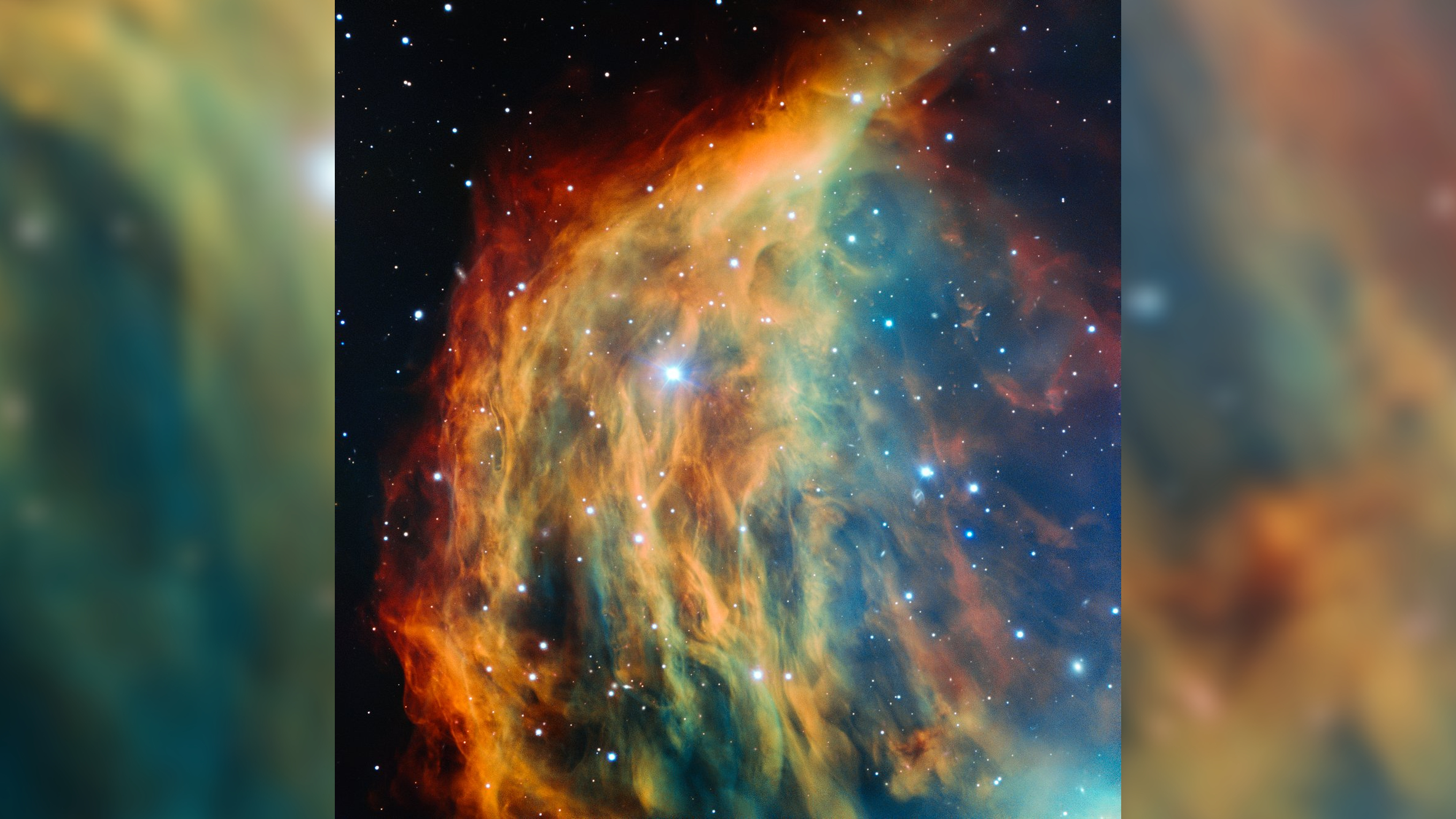

Medusa Nebula (Abell 21)
Magnitude: 15.99
Approximate distance from Earth: 1,500 light-years
Location: 7h 29m 3s (correct ascension), +13°14’48” (declination)
The faint Medusa Nebula was discovered by astronomer George O. Abell in 1955, in accordance with Astronomy Trek. The planetary nebula, which formed when a crimson massive star transitioned proper right into a white dwarf, is roughly 4 light-years all through.
NGC 2392
NGC 2392
Magnitude: 9.9
Approximate distance from Earth: 5,000 light-years
Location: 7h 29m 11s (correct ascension), +20°54’42” (declination)
NGC 2392 has a unimaginable spherical kind. The planetary nebula is known by quite a few nicknames, primarily probably the most well-known of which isn’t used on account of its discriminatory nature; you could be taught further regarding the nickname in a NASA assertion.
Jellyfish Nebula (IC 443)
Jellyfish Nebula (IC 443)
Magnitude: 12
Approximate distance from Earth: 5,000 light-years
Location: 6h 17m 13s (correct ascension), +22°31’5″ (declination)
The Jellyfish Nebula is a 70-light-year-wide remnant of a supernova that is estimated to be between 3,000 and 30,000 years earlier, per Astronomy Trek.
Geminid meteor bathe
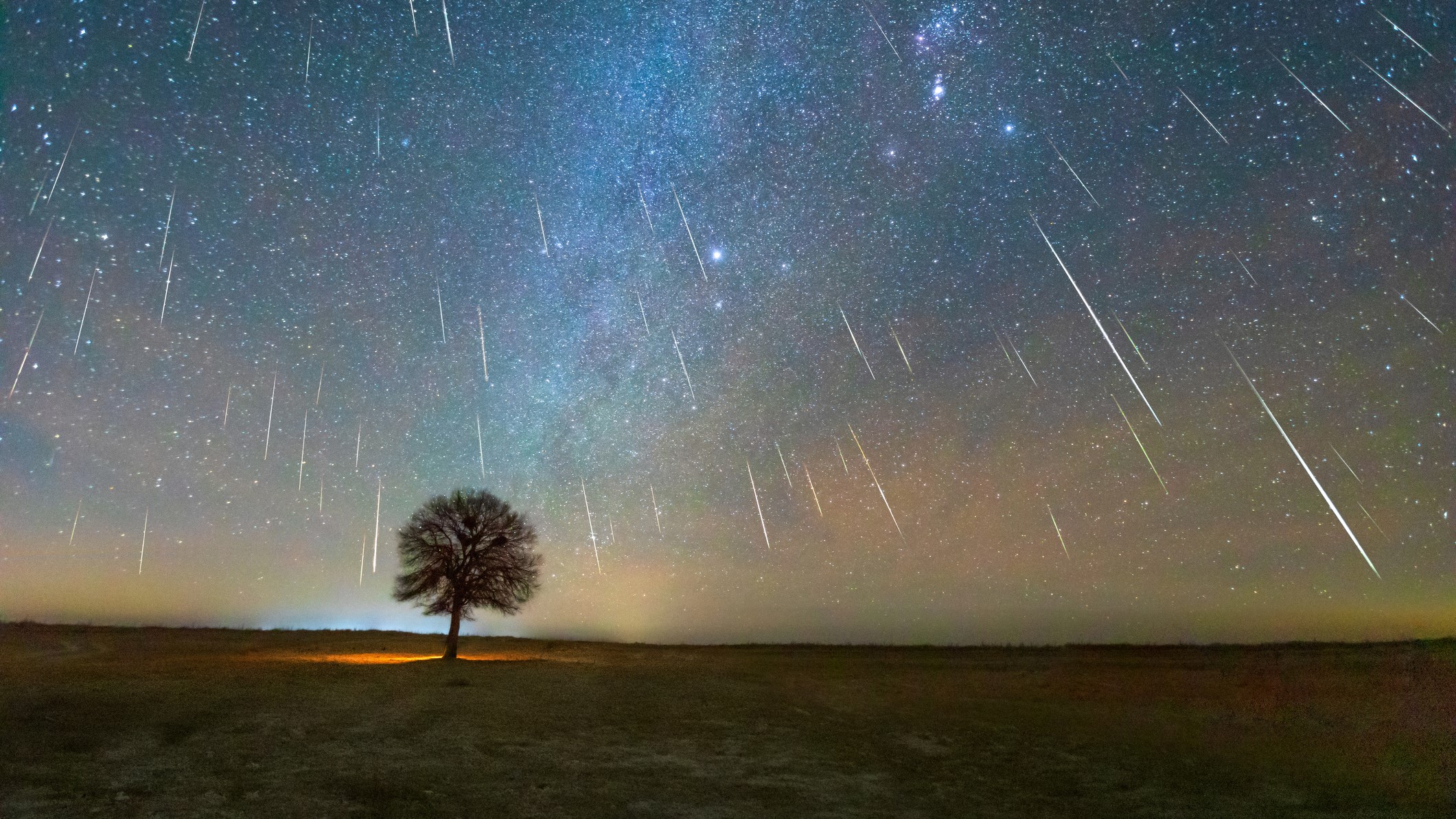

The Geminid meteor bathe is no doubt probably the most prolific meteor showers of the yr, with a charge of 120 meteors per hour all through its peak, in accordance with NASA. The bathe occurs between Nov. 19 and Dec. 24 with a peak spherical Dec. 14. Though the bathe originates from the particles path of asteroid 3200 Phaethon, its radiant degree (that is, the aim from which the meteors appear to emanate), is throughout the constellation Gemini.
Mythology
Castor and Polydeuces, or Pollux in Latin, had been twin brothers in Greek mythology born to Queen Leda of Sparta and two fathers: King Tyndareus of Sparta and the god Zeus. As such, Castor was mortal and Pollux was immortal, in accordance with the Chandra X-ray Observatory. The inseparable duo was known as the Dioscuri. All through a familial dispute (or possibly in battle), Castor was killed, nevertheless Pollux shared his immortality alongside along with his brother so that they might very nicely be collectively perpetually.
Gemini constellation FAQs answered by an expert
We requested Mike Reed, an astronomer and a distinguished professor throughout the Division of Physics, Astronomy and Provides at Missouri State Faculty, a few steadily requested questions regarding the Gemini constellation.

Distinguished Professor throughout the Division of Physics, Astronomy and Provides at Missouri State Faculty.
The place is the Gemini constellation?
All through July, the photo voltaic is true in the midst of Gemini, so it may well’t be seen at evening time. Being a sign of the zodiac, Gemini will journey all through the sky to the south as a result of the Earth spins, for these of us north of the Tropic of Most cancers. It is between Most cancers and Orion/Taurus, with the horns of Taurus pointing to it and being above Orion’s head.
How will you uncover the Gemini constellation?
Seek for it throughout the fall and winter. Gemini has two shiny stars, which can be named Castor and Pollux, twins of Greek mythology. The celebrities symbolize the eyes of the twins with their ft merely dangling throughout the Milky Technique. Pollux’s correct foot is the star Alhena, a shiny star correct in line between the even brighter stars Pollux and crimson Betelgeuse in Orion.
What variety of stars are throughout the Gemini constellation?
Even in shiny areas, when you possibly can see stars, you’re in all probability to have the flexibility to see Castor and Pollux. From a reasonably darkish website, you may even see a few dozen stars, which make the twins appear as stick figures holding palms. The two shiny stars Castor and Pollux are the eyes of the twins, nevertheless apparently, Castor is certainly six stars so distant they appear as one. It has two shiny ones and 4 very dim ones, all gravitationally positive and touring collectively. Being shut throughout the sky to the Milky Technique, Gemini has quite a few open star clusters and nebulae.
Additional belongings
Study the story behind the names of the Gemini twins from the Chandra X-Ray Observatory. Be taught regarding the twin stars Castor and Pollux from NASA. Watch a video regarding the Geminid meteor bathe by the Museum of Science, Boston.
Bibliography
Deep-Sky Objects in Gemini. Astronomy Trek. Retrieved July 9, 2023, from https://www.astronomytrek.com/deep-sky-objects-in-gemini/
Geminga. Britannica. Retrieved July 9, 2023, from https://www.britannica.com/place/Geminga
Gemini. Britannica. Retrieved July 9, 2023, from https://www.britannica.com/place/Gemini-constellation-and-astrological-sign
Gemini Constellation. Constellation Data. Retrieved July 9, 2023, from https://www.constellation-guide.com/constellation-list/gemini-constellation/
Geminids. NASA. Retrieved July 9, 2023, from https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/asteroids-comets-and-meteors/meteors-and-meteorites/geminids/in-depth/
Messier 35 – A cluster of stars. European Southern Observatory. Retrieved July 9, 2023, from https://www.eso.org/public/italy/images/b10/?lang
NASA to Reexamine Nicknames for Cosmic Objects. NASA. Retrieved July 9, 2023, from https://www.nasa.gov/attribute/nasa-to-reexamine-nicknames-for-cosmic-objects
Stargazing Gemini the Twins. Milwaukee Astronomical Society. Retrieved July 9, 2023, from https://milwaukeeastro.org/Stargazing/gemini.asp